Lies, Damned Lies, and Suzanne Humphries (Part 1)
A Painfully Detailed Look at a Factually Bankrupt Episode of the Joe Rogan Experience
Owing to the length, this post is split into 2 parts.
Introduction
Make no mistake, the recent appearance of Dr. Suzanne Humphries on The Joe Rogan Experience podcast—which reaches an astronomical 11 million listeners per episode—represents a public health emergency that demands an urgent, forceful and unified response. While we might typically ignore fringe medical opinions, the sheer scale of this platform and the numerous falsehoods propagated by this guest throughout the whole duration of this lengthy segment transforms Humphries's dangerous views, rooted in blatant falsehoods and mischaracterization of data, into a potential public health disaster. This all while the country faces one of the worst measles outbreaks in recent history.
This appearance follows Rogan's troubling pattern of platforming pseudoscience to his massive audience. From hosting notorious HIV/AIDS denialist Peter Duesberg, whose theories led to catastrophic policies in South Africa resulting in an estimated 330,000 preventable deaths , to promoting ivermectin for COVID-19 treatment against FDA warnings, to interviewing Bret Weinstein who falsely claimed ivermectin alone could drive COVID-19 to "extinction" NPR , to repeatedly platforming conspiracy theorist Alex Jones —Rogan has consistently amplified dangerous misinformation under the guise of "just asking questions" while reaching millions of listeners per episode.
First, a note on the length of this analysis
It is not our expectation that anyone read this discussion in its entirety (although sincere kudos if you do) - we understand you have lives and priorities. It took six scientists and countless hours to review the claims, dig into the evidence, and formulate this detailed response. The purpose of a post of this length is multi-faceted:
It demonstrates the sheer volume of misinformation that can be presented in a single episode of Joe Rogan's podcast without challenge from a knowledgeable expert.
It illustrates Brandolini's Law: The effort required to refute false information is orders of magnitude greater than the effort needed to produce it (and in our estimation, the "10x" figure is conservative).
It serves the public interest: People deserve accurate information to inform their health decisions. Ignoring misleading commentary that could affect these decisions would be a disservice to public health.
The anti-vaccine movement frequently elevates individuals with credentials who present information that contradicts the scientific consensus. Suzanne Humphries, despite her background in nephrology, presents claims about vaccines that diverge dramatically from established medical evidence and consensus. While her medical degree might appear to lend authority to her statements, this analysis will demonstrate how her assertions consistently contradict peer-reviewed research and misrepresent scientific and medical history.
Humphries, despite her board certification in nephrology (she has failed to renew her certification as of 2022), has abandoned evidence-based medicine to become one of the most prominent voices in the anti-vaccine movement. After practicing medicine (medical practice rooted in rigorous scientific evidence and consensus) from 1989 to 2011, she pivoted to what she misleadingly describes as "research into vaccines, immunity, history, and functional medicine." Her 2013 book, "Dissolving Illusions," has become a cornerstone text for anti-vaccine advocates despite being built on a foundation of distorted data, cherry-picked studies, and fundamental misrepresentations of medical history.
Former anti-vaccine advocate Heather Simpson notes Humphries's work is deceptively convincing: "She uses fancy graphs to prove that diseases were already declining due to clean water and sanitation when vaccines were introduced. She did such a compelling job at backing up her argument, that unless you really dug into the other side of the story, one could easily believe her."
What makes Humphries particularly dangerous is her exploitation of legitimate medical credentials to lend false credibility to thoroughly debunked claims. Her supposedly scientific arguments are methodically designed to sow doubt about one of medicine's greatest achievements. The consequences are not theoretical—they directly contribute to declining vaccination rates, resurgent outbreaks of preventable diseases, and needless suffering and death.
As scientists committed to evidence-based medicine and public health, we feel we have a professional obligation to expose and counter this dangerous misinformation. This interview demands our strongest possible response, not simply to correct the record, but to protect public health from claims that directly threaten the lives of vulnerable populations.
Key Misinformation and Corrections: Alternative Medicine Claims
Claims About Cinnamon for Glycemic Control (00:14-02:51)
Claim: Humphries stated that "Cinnamon is a powerful herb, actually, and it's known to be helpful in glucose handling for a lot of diabetics taking it in capsule form now."
Reality: Cinnamon is delicious but… while some research does suggest cinnamon may offer minor benefits for glycemic control, characterizing it as "powerful" fundamentally misrepresents the scientific consensus. A comprehensive review of 11 randomized controlled trials published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics found only modest reductions in fasting plasma glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels—with most studies failing to reach American Diabetes Association treatment goals.
The average HbA1c reduction was merely 0.49%, far below the 1.0% reduction needed to achieve clinically significant protection against complications. Study authors explicitly warned that clinicians should continue recommending established treatments rather than cinnamon.
This pattern of exaggeration is emblematic of Humphries's approach throughout the interview—selectively presenting fragments of truth while dramatically inflating their significance, potentially leading vulnerable patients to abandon proven medical treatments in favor of inadequate alternatives with potentially life-threatening consequences.
🧠 Bottom line: Cinnamon is not a “powerful herb” that can replace diabetes medication. At best, it’s a mild adjunct—and even that benefit is limited and inconsistent across studies. Presenting it otherwise is misleading and potentially harmful.
Vitamin A and Measles Vaccines (02:51-03:42)
Claim: Joe Rogan stated that measles vaccines deplete vitamin A levels, and Humphries reinforced this concern.
Reality: This is a profoundly misleading statement of the evidence. Studies do show a transient decrease in serum vitamin A levels following measles vaccination, similar to what happens during natural measles infection. However, this effect is temporary and resolves within a month. Importantly, the research shows that:
Most critically, vitamin A levels remained within normal clinical ranges throughout the process—never dropping to levels that would cause any clinical concern.
Vitamin A is a negative acute phase reactant - it naturally declines whenever there is an inflammatory response, not just with measles vaccine.
Serum vitamin A measurements don't necessarily reflect total body vitamin A reserves stored in hepatic stellate cells.
Most damning to her argument is the complete absence of any documented cases of vitamin A deficiency diseases following measles vaccination in the medical literature—something that would certainly exist if her implications were valid.
This is textbook misinformation: taking an isolated laboratory finding, stripping it of all medical context, and presenting it to suggest a non-existent health risk. Such manipulation of scientific data is not a matter of differing opinions—it represents a dangerous distortion of medical evidence with potential to harm public health.
🧠 Bottom line: Claims that measles vaccination causes vitamin A deficiency are misleading and omit key context. Temporary, mild decreases in serum vitamin A are a normal response to inflammation and do not indicate a deficiency or health risk.
Claim: Humphries suggests that people should get vitamin A supplementation if they receive the measles vaccine.
Reality: WHO recommends that vitamin A be given with measles vaccination in lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where there is a high prevalence of vitamin A deficiency and there are limited encounters with the healthcare system to enable regular follow-up care. However, this is given to address the high burden of vitamin A deficiency, not because measles vaccination meaningfully reduces vitamin A levels. Moreover there is some nuance to the use of vitamin A supplementation at the same time as measles vaccination: some work has found that giving both at the same time can reduce the immune response to the measles vaccine in young children, compromising their protection. This makes sense- vitamin A has a direct antiviral effect on measles (and the attenuated vaccine virus has to replicate a little bit in the body to induce an effective response) and also induces regulatory T cells that block inflammation that can facilitate an effective immune response. Nonetheless, multiple studies find that vitamin A supplementation alongside measles vaccination does substantially reduce the immune response, and in some cases may enhance it (though those reporting enhancement of the response are in countries with high levels of vitamin A deficiency). Still, in the setting of vitamin A sufficiency, it probably does not make much sense to give supplemental vitamin A with measles vaccines given the totality of evidence.
More concerning is that Humphries also fails to acknowledge the very real risks associated with vitamin A toxicity, which we are seeing the effects of in real time in Texas. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning excess amounts are stored in the body rather than excreted, which can lead to a dangerous condition known as hypervitaminosis A. Symptoms can range from headaches, dizziness, and nausea to liver damage up to and including liver failure requiring transplant, intracranial pressure, and even death in severe cases. In children, excess intake can cause bone abnormalities and growth disturbances.
By promoting unnecessary supplementation without addressing these risks—or the actual clinical contexts in which vitamin A is beneficial—Humphries once again selectively presents information in a manner reflecting a wanton attempt to mislead people or profound clinical ineptitude.
🧠 Bottom line: Vitamin A supplementation with measles vaccination is recommended in LMICs where deficiency is common, not because the vaccine depletes vitamin A. Supplementing in vitamin A-sufficient populations could potentially reduce the effectiveness of the vaccine, and indiscriminate use of vitamin A can cause significant toxicity, particularly in children. Misrepresenting this nuance is misleading and potentially harmful.
Claim: Humphries suggests that vaccinated children end up getting more antibiotics.
Reality: It is true that overuse of antibiotics causes significant harm, for reasons that go far beyond just the threat of antimicrobial resistance (although that is a major concern). For instance, antibiotic use in childhood has been associated with reduced antibody responses to vaccines. Antibiotic courses are also often arbitrary in length and there is a major push to reassess whether shorter courses are noninferior to longer ones (thus far, the studies consistently say yes)- more exposure to antibiotics means a higher risk of toxicity which can be quite serious depending on the specific antibiotic (cephalosporins can cause seizures, aminoglycosides can cause hearing loss and can harm kidneys, etc.). Antibiotics are absolutely lifesaving, but owing to these factors, it is absolutely in the best interest of public health to restrict use of antibiotics only to circumstances where their use necessary.
However, Humphries has it quite backwards regarding who gets more antibiotics. Firstly, there is a remarkably consistent, strong inverse relationship between influenza vaccine uptake and antibiotic prescriptions (here, here, here, here, here, and here). Rotavirus vaccination has also been associated with reduced antibiotic prescriptions. The near elimination of Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b) has drastically reduced antibiotic prescriptions for this disease, as is the case for pertussis and pneumococcal disease. Another study found that in Denmark, the rollout of the first vaccination program and updated prescribing guidelines reduced antibiotic prescriptions, but these fell even more with the introduction of the second vaccination program.
Fundamentally, vaccines are critical tools in helping us to curb the threat of antimicrobial resistance.
🧠 Bottom line: While overuse of antibiotics poses public health risks, including antimicrobial resistance and toxicities from the antibiotics themselves, vaccines help reduce antibiotic use. Vaccinations against influenza, rotavirus, Hib, pertussis, and pneumococcal disease are consistently associated with decreased antibiotic prescriptions. Therefore, vaccines play a crucial role in combating antimicrobial resistance by preventing infections that would otherwise require antibiotics. Humphries’s claim that vaccines increase antibiotic use is factually incorrect.
Tylenol and Vaccine Responses (02:51-03:42)
Claim: Tylenol causes all sorts of immunological disturbances that interfere with the vaccine.
Reality: This statement grossly exaggerates limited research findings to frighten parents. While antipyretic medications have been observed to reduce antibody responses to some vaccines if given before vaccination, Humphries fails to disclose several crucial facts that completely change the interpretation:
Any blunting of antibody responses is corrected with booster doses as per normal vaccine schedules.
Reduced immune responses have only been observed when antipyretics were given simultaneously with vaccinations—not afterward.
The clinical significance of these findings (whether they actually translate to lower protection) remains unclear and unproven.
Fever is indeed part of the natural immune response and is associated with metabolic changes that enhance immunity across many cell types; for this reason AAP has noted that fever-reducing medications be given to improve hydration and comfort, not simply to lower temperature. Guidelines do advise against giving antipyretic medications like NSAIDs and Tylenol (acetaminophen) before vaccination, but they explicitly state it is appropriate to give them after if symptoms cause significant discomfort.
While Tylenol can be dangerous at higher doses because it can cause potentially fatal liver injury, it does not cause the broad "immunological disturbances" Humphries dramatically claims. There is some evidence that patient taking immune checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapies for cancer may be best served by avoiding acetaminophen because it associates with poorer response to the immunotherapy, but the generalizability of this finding is unclear, and existing data on antipyretic use with vaccination generally show no substantial effect.
By framing established medical knowledge in the most frightening possible light, Humphries demonstrates a pattern of weaponizing partial information to undermine confidence in both vaccines and routine medical care.
🧠 Bottom line: While giving antipyretics before vaccination may slightly reduce antibody responses, booster doses correct this, and the clinical impact is unclear. Post-vaccination antipyretic use for symptom relief remains appropriate. Alarmist claims about antipyretics causing “immunological disturbances” are misleading and not supported by the available evidence.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (03:42-06:40)
Claim: Humphries alleges "massive variation exists in drug manufacturing at the point of delivery to the public, which accounts for the breadth of responses to the drugs."
Reality: This claim is demonstrably false and reveals either profound ignorance or deliberate misrepresentation of pharmaceutical manufacturing regulations. Every drug must undergo strict lot-to-lot consistency studies to ensure uniform composition under Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) requirements strictly enforced by regulatory agencies like the FDA.
To ensure the safety of specific batches released, manufacturers must perform tests that prove the purity, potency, identity and sterility. Lots cannot be released until the FDA releases them after performing confirmatory testing of the lots. This system ensures pharmaceutical consistency at a level that would be impossible for the unregulated supplements Humphries often promotes.
Variation in the response to drugs is principally explainable by pharmacogenetics, as well as specific health conditions individuals may have. For example, impaired liver function can drastically alter metabolism of drugs, either enhancing or reducing the effect depending on the specific drug. Similarly, drugs that are eliminated by the kidneys will have prolonged retention in the body in the setting of reduced kidney function, which can influence their effects and toxicity. As for genetics: there are a series of enzymes mainly found in the liver known as the CYP family, and these can vary hugely across individuals. For example, CYP2C19 has a variant known as CYP2C19*17 which causes people to metabolize drugs (or prodrugs) that are substrates for CYP2C19 extremely rapidly, thought to be because this variant forms a binding site for the GATA family of transcription factors, which cause it to be expressed extensively.
The irony is striking: Humphries criticizes pharmaceutical manufacturing while remaining silent about the supplements industry—including products like Joe Rogan's Alpha BRAIN®—which operates under far looser production standards with weak, inconsistent, or absent efficacy data (in part because without a regulatory apparatus demanding efficacy studies, essentially no company is going to bother with the expense of conducting trials). This striking double standard reveals a clear bias against evidence-based medicine rather than a genuine concern for manufacturing consistency. For the record, Rogan’s Alpha BRAIN®, is a dietary supplement that claims to support cognitive functions, including memory, mental speed, and focus, based on a very underpowered Phase 2 study showing modest improvement in one measure (with questionable outcomes) of cognitive performance in 30 young, highly educated, high-functioning adults (BTW, cognitive decline is most common in 65+).
This pattern of misrepresenting basic regulatory facts while promoting less regulated alternatives demonstrates how Humphries consistently undermines evidence-based medicine while tacitly supporting industries with far less quality control and scientific scrutiny.
🧠 Bottom line: Claims that pharmaceutical manufacturing lacks consistency are false. Drugs undergo rigorous CGMP compliance and lot-to-lot testing. Variability in drug response is primarily due to variation in genetics and health conditions, not manufacturing inconsistencies. In contrast, the supplement industry, which Humphries often supports, lacks comparable regulation and oversight.
History of the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act (NCVIA) (03:42-06:40)
Claim: Humphries greatly misrepresents the history and purpose of the NCVIA, claiming it came about because of the flu vaccine-induced GBS cases in 1976.
Reality: Humphries makes multiple fundamental errors in her discussion of the NCVIA. First, she brings up the case of the 1976 influenza vaccine causing Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). This was an extremely rare outcome, and while there was an increased risk, it has not been reproduced with other seasonal flu vaccines and influenza infection drastically increases the risk of GBS; on the other hand, a recent meta-analysis determined that seasonal influenza vaccination reduces the risk of GBS by 88%, and a 2022 WHO position statement asserts that the net effect of the flu vaccine on GBS is a reduction in risk. She also describes the vaccine as live attenuated or a subunit. The 1976 flu vaccine was an inactivated vaccine- it is neither live attenuated or a subunit. She then claims that this very rare risk of GBS is what enabled the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act (NCVIA; a law that establishes the no-fault compensation system for people harmed by vaccines) to be passed in 1986. But the NCVIA had nothing to do with the GBS cases from the 1976 flu vaccine as Humphries claimed.
The basis of the lawsuits that led to the NCVIA was the claim that DTP vaccines (the vaccines here are the whole-cell pertussis vaccines which are no longer used in the US) caused an encephalopathy syndrome in children. Subsequent investigation proved this to be wrong and found genetic epilepsies as etiologies for these conditions, in which a fever can trigger seizures. The DPT vaccines were among the first triggers for fever in these children, so an association was made. However, these children would have developed seizure disorders regardless of whether or not they received DTP vaccine- but if they hadn’t, they would be at markedly higher risk of contracting diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
The reason for the NCVIA was that fighting these lawsuits was costing pharmaceutical companies more than their profits on vaccines, so we got to a point of having just one vaccine manufacturer for DPT vaccines who was about to stop production. This would have meant no more DTP vaccines and no protection against three deadly diseases. That's where the federal government stepped in and decided to established the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (NVICP): a no-fault compensation system where vaccines would have an excise tax on every dose used to compensate those who had been harmed by a vaccine after review of their case by a special master. Furthermore, in contrast to actual criminal court, where you need to prove beyond a reasonable doubt, all that is needed for compensation via the NVICP was to show a plausible mechanism between the vaccine and the adverse event (sometimes described as 50% and a feather burden of proof). It also led to the creation of “injury tables” which described adverse events that would automatically be compensated if they occurred in the relevant time frame. The NCVIA was passed with input from Barbara Loe Fischer, an ardent anti-vaccine activist who remains active today as a leader in the anti-vaccine organization NVIC, which is ironic given all the bellyaching from the anti-vaccine lobby about the law.
Humphries claims that you can only be compensated by the NVICP if you have a table injury. This is false. If you develop a table injury in the specified time frame, you are AUTOMATICALLY compensated. Others can still receive compensation if they can demonstrate a plausible link between the vaccine and the adverse event.
🧠 Bottom line: Humphries falsely links the NCVIA to the 1976 flu vaccine and misrepresents how the compensation system works. The NCVIA was established in response to DTP vaccine lawsuits, not flu vaccine cases. Compensation through the NVICP does not require a table injury—such injuries guarantee compensation, but other claims can still be compensated if a plausible link is shown.
Vaccine Adjuvants (03:42-06:40)
Claim: Vaccines contain "all sorts of horrid things added to it."
Reality: This inflammatory, fear-mongering statement is made without specifying a single ingredient—a classic tactic designed to generate fear rather than promote informed decision-making. Humphries employs vague, emotionally charged language about "horrid things" while providing zero scientific context.
The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia's Vaccine Education Center explains that vaccine ingredients fall into specific categories with defined purposes:
antigens (the active components that generate immunity)
adjuvants (substances that enhance immune response and ensure the correct type of response occurs)
stabilizers (to maintain vaccine integrity during storage)
preservatives (to prevent contamination in multi-dose vials)
and manufacturing byproducts (purified out, but may be present in minute quantities because it is impossible to completely purify everything).
The most commonly used adjuvant in human vaccines is aluminum salts, which have been used for nearly a century with an extraordinary safety record. It wasn't until the mid-1990s that vaccines using a virosome adjuvant (i.e., particles that structurally resemble viruses and can therefore trigger the immune system’s responses to repetitive structures) appeared, making them the first widely used vaccines not adjuvanted with aluminum. See this deep dive on aluminum salts for more details. A major reason it took so long to develop different adjuvants wasn't safety concerns with existing ones—it was because scientists didn't fully understand what properties were needed for effective adjuvants beyond safety. The approach was completely empirical (i.e., try whatever and see what works- even breadcrumbs were used at one point), not driven by safety concerns with existing adjuvants.
Humphries's deliberate vagueness combined with emotionally loaded language represents a textbook example of anti-vaccine rhetoric designed to create fear rather than understanding.
🧠 Bottom line: Humphries's vague and emotional statements about vaccine ingredients lack scientific basis and are intended to provoke fear. Vaccine ingredients serve specific, well-studied purposes, with adjuvants like aluminum salts having a long history of safe use. Claims to the contrary are misleading and unsubstantiated.
Claim: Humphries asserts that all non-live vaccines are adjuvanted with aluminum.
Reality: This statement is demonstrably false and reveals a troubling ignorance of basic vaccine composition. Humphries is correct that live vaccines are not adjuvanted with aluminum salts, because they are self-adjuvanting. However, it is categorically not true that every non-live vaccine is adjuvanted with aluminum.
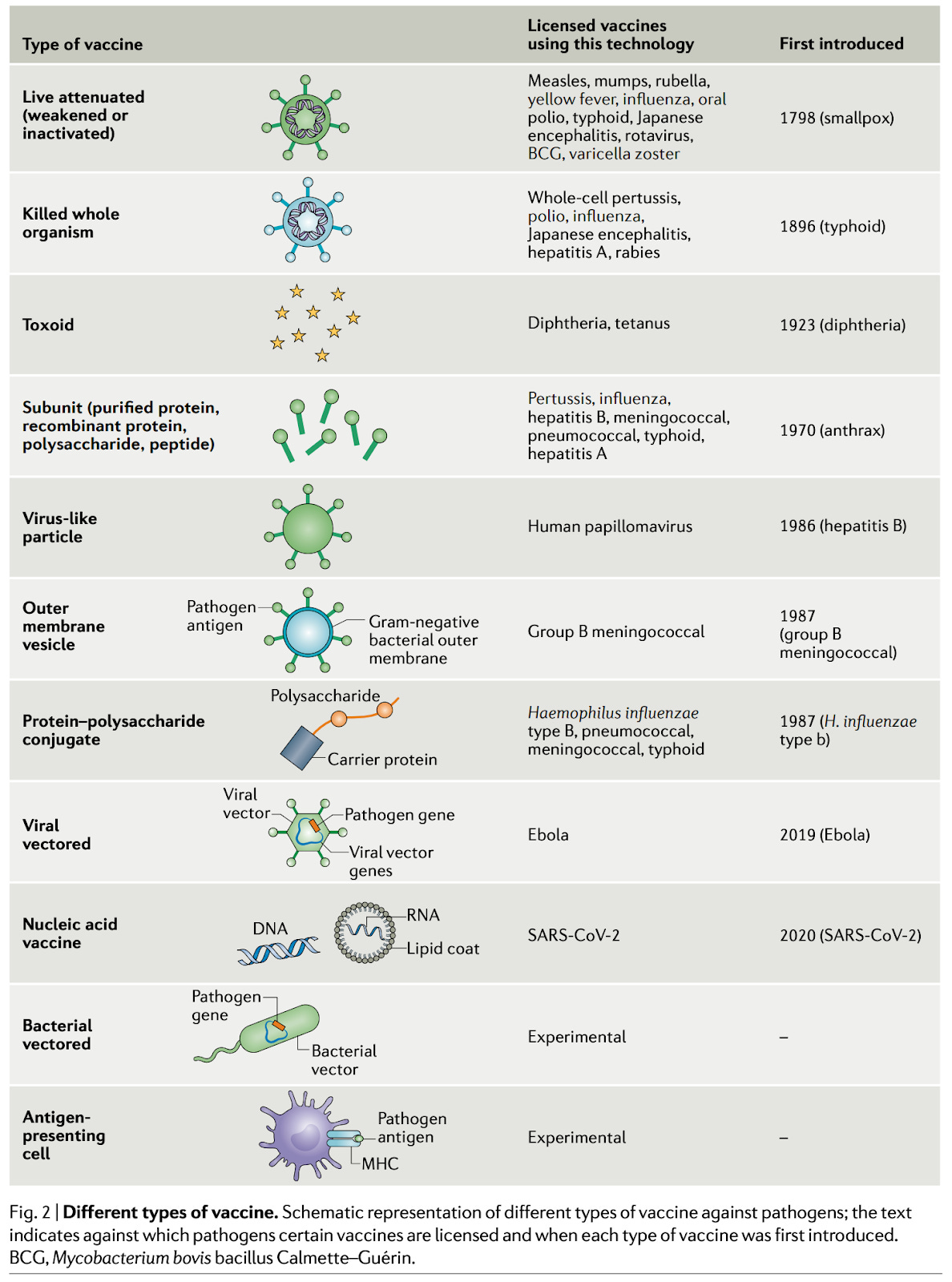
Here’s a list of some examples of vaccines in the US not adjuvanted with aluminum and not live:
Influenza vaccine: 3 non-live types:
Whole inactivated split virions (high-dose and standard dose): no adjuvant
Recombinant hemagglutinin subunit: no adjuvant
Adjuvanted whole inactivated: MF59 (an oil-in-water emulsion)
Inactivated polio vaccine (IPV): no adjuvant
Combination vaccines including IPV may be adjuvanted with aluminum salts.
mRNA vaccines: mRNA is self-adjuvanting (not completely immunosilent despite N1-methylpseudouridine substitutions), but most of the adjuvant activity arises from the ionizable lipid component of the lipid nanoparticle
Recombinant protein vaccine: adjuvanted with Matrix-M (a saponin-based immune stimulating complex derived from the soap bark tree)
Recombinant glycoprotein E subunit: adjuvanted with AS01B
RSV:
mRNA vaccine: RNA is self-adjuvanting (not completely immunosilent despite N1-methylpseudouridine substitutions), but most of the adjuvant activity arises from the ionizable lipid component of the lipid nanoparticle
Recombinant prefusion-stabilized F protein subunit: no adjuvant (Abrysvo), or AS01E a lower dose AS01 than AS01B; used in Arexvy)
Nirsevimab is an RSV monoclonal antibody used as passive immunotherapy; it is not a vaccine, but regardless, contains no adjuvant.
No adjuvant
Mpox vaccines are considered live but the vaccine itself is only capable of replicating in specific cell lines because Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA- the virus in the vaccine) missing huge chunks of its genome- it does not replicate within the human body and so is functionally an inactivated vaccine.
This basic factual error undermines Humphries's credibility as an authority on vaccine composition and safety. It is also especially surprising that she would make this error in light of the fact that she used to be a nephrologist, because aluminum toxicity principally occurs only in people with severely depressed kidney function.
🧠 Bottom line: Not all non-live vaccines contain aluminum adjuvants. Many vaccines—including some influenza, polio, COVID-19, shingles, RSV, and Mpox vaccines—do not use aluminum salts. Humphries's claim to the contrary is factually incorrect and demonstrates a fundamental misunderstanding of vaccine composition.
Claim: Humphries claims, "And that [aluminum] is very well known to trigger that Th2 response, which is the allergic response, which can set up your body for autoimmunity."
Reality: This statement represents a profound misunderstanding or deliberate misrepresentation of immunology. This takes a minute to unpack, so please bear with us.
Many people conceive of the immune system as an on/off switch or a dial: when it's on, everything is as it should be, and when it's off, bad things happen. However, rather than being an on/off dial, the immune system is more like an extremely sensitive gear shift which can sense intermediate positions between particular gears and with each gear having a distinct purpose and function.
One of the earliest concepts for the function of the immune response was known as the Th1/Th2 model. It comes from studies of leprosy infection. Scientists observed two distinct T cell types that had distinct immune responses, which they labeled "Th1" (type 1) and "Th2" (type 2). With this model, scientists initially suggested that type 1 immunity was important for dealing with microbes that get inside cells, emphasizing a T cell response from cells they called T helper 1 cells (Th1), while type 2 immunity was important for dealing with microbes that are found outside cells, emphasizing an antibody response through helper T cells they called T helper 2 cells (Th2). Eventually, immunologists began to classify certain autoimmune diseases as being Th1 or Th2 predominant.
This model, which Humphries relies on, is extremely outdated (and she also gets basics about it wrong) and has been replaced with much more granular classifications that do have importance. For simplicity, we generally classify immune responses as type 1, type 2, and type 3, but this does not capture the whole breadth of immune responses.
Today we recognize at least six additional types of helper T cells, not just two, including:
Th17 cells (associated with type 3 immunity for responses against extracellular bacteria, especially at mucosal barriers)
Regulatory T cells (which limit inflammation and enforce immune tolerance)
Follicular helper T cells (critical for producing high-quality antibodies)
Th22 cells (protection at barriers and wound healing)
Th9 cells (antitumor and pro-allergenic)
CD4 CTLs (CD4 T cells that kill infected cells directly, like CD8 T cells)
And numerous subtypes of each (for example, Th2 cells that drive allergy are Th2A cells; TFH cells can be specialized for type 1, 2, 3, or suppression of immune responses so these are known as TFH1, TFH2, TFH17, TFR etc.)
Most critically for Humphries's claim, we now know that most autoimmune diseases are primarily driven by Th17 cells, not Th2 cells as she claims (which, to be clear, is not even what the Th1/Th2 model for autoimmune diseases argued; it argued that some autoimmune diseases were Th1-predominant and some were Th2-predominant, and most are Th1 predominant).
Additionally, the idea that Th2 responses are simply "allergic responses" is a gross oversimplification. Type 2 immunity serves crucial protective functions against parasites and venoms, mainly dedicated to expelling the threat because it cannot really be killed effectively (worms are too large, venoms aren’t alive), and also plays roles in wound healing and tissue repair.
Furthermore, Humphries incorrectly implies that only Th2 responses generate antibodies, while modern immunology understands that robust antibody responses occur with each flavor of the immune response—they simply produce different antibody classes optimized for different threats.
Now you might be wondering- do we really need such complicated models to understand the immune system? Fair enough- the models become byzantine as you dig into the details, but the complexity that they are simplifying is critical to improving treatments for diseases of the immune system and for vaccines. For example, a key limitation of the pertussis vaccines is that they induce Th2 immune responses which are not particularly great at clearing pertussis bacteria in the event of infection, contributing to an asymptomatic carrier state. We now understand that pertussis vaccines would work much better if they elicited a balanced type 1 and type 3 response and are working towards better pertussis vaccines to do just that. Similarly, many autoimmune diseases are driven by specific cytokines and we have biologic therapies to target just these cytokines. In the past, we would simply have thrown corticosteroids at patients, and while this is still sometimes necessary today, it can involve major risks and side effects that are avoided with precision targeting of individual cytokines.
🧠 Bottom line: Humphries is using an outdated and oversimplified model of immunity from the 1980s to make alarming claims about aluminum in vaccines, and, amazingly, she doesn’t even seem to understand the model she references. Modern immunological science has moved far beyond this model, recognizing a far more complex and nuanced immune system, which has enabled the development of precision treatments for autoimmune diseases by targeting specific cytokines that occur with autoimmune diseases, instead of a sledgehammer approach with corticosteroids (although these can also have a critical role). Her fundamental mischaracterization of basic immunology undermines her credibility when discussing vaccine ingredients and their alleged effects.
Claim: Humphries promotes an oversimplified view that Type 1 (Th1) immunity is "better" than Type 2 (Th2) immunity and that vaccines disrupt this balance.
Reality: Type 1 and type 2 immunity are not rankable on a hierarchy as to which one is better. This is like saying that butter is better than a bowling ball. You wouldn’t use these in the same context, so how can you compare which one is better? The same is true of type 1 and type 2 immunity. We evolved these types of responses for different types of threats. Using type 1 immunity would not be particularly helpful to deal with a worm, or even surviving pregnancy as a fetus. Using type 2 immunity could be disastrous if infected with a respiratory virus.
🧠 Bottom line: Humphries incorrectly portrays Type 1 (Th1) immunity as inherently "better" than Type 2 (Th2) immunity, creating a false dichotomy that has been rejected by modern immunology. Both types serve crucial protective functions against different threats. Her oversimplified model ignores decades of immunological advances that have identified at least 8 major classes of helper T cells with complex interactions. Humphries's comments on this matter are both baseless and profoundly ignorant..
Placebo-Controlled Vaccine Studies (06:12-06:40)
Claim: There are no saline placebo studies of vaccines.
Reality: This is demonstrably false. Numerous vaccines have undergone placebo-controlled trials, including studies using saline placebos. Multiple resources document these studies, including analyses from Vaxopedia and The Unbiased Science Podcast.
A group of WHO experts has written a detailed guide on how placebos should be used in vaccine trials. For second-generation vaccines or other situations where withholding protection would be unethical, active comparators may be used instead, which is ethically mandated by the Common Rule, the Declaration of Helsinki, and Good Clinical Practice guidelines. In addition to the ethical aspect to it (that is never ethically acceptable to withhold the standard of care) there is no point in a next-generation medical product that does not work as well or better than the previous generation or does not have some kind of safety advantage. Comparing directly to the standard of care gives more useful information.
In some cases, rather than using a placebo, researchers compare to another vaccine not expected to induce protection. This is done because the reactogenicity helps preserve blinding, and there is a chance that the unrelated vaccine could offer some nonspecific protection, helping to ensure the safety of the placebo group, though that could lead to underestimation of the vaccine’s efficacy.
This approach is not unique to vaccines but reflects established ethical principles in all areas of medicine. The Declaration of Helsinki, which sets ethical guidelines for medical research, explicitly states that new interventions should be tested against the best proven intervention.
There are some important exceptions to the requirement for randomized controlled trials of vaccines. One is the animal rule. In essence, there are some diseases that are so dangerous that subjecting humans to the risk of contracting those diseases cannot be ethical. In these situations, efficacy is assessed by immunizing (or medicating, if you’re looking at a drug) a relevant animal whose physiology is similar to a humans and confirming that the vaccine is protective. This is how the anthrax vaccine was approved.
In addition to this, it is sometimes infeasible to do a field trial of a vaccine. Chikungunya epidemics for example are extremely rapid to the point that setting up a field efficacy trial is not practical, so the chikungunya vaccine was approved without a phase 3 efficacy trial because it would not be feasible to get data through the field trial, instead relying on seroresponse rates to the vaccine and challenge studies on monkeys demonstrating its effectiveness.
Controlled human infection models (CHIMs) are also a proposed means by which one can get a vaccine approved. This involves vaccinating individuals and then after a suitable interval of time, directly challenging them with the microbe the vaccine is to protect against. The cholera vaccines Vaxchora was approved through this method.
🧠 Bottom line: Many vaccines have undergone placebo-controlled trials, including those using saline placebos. Ethical guidelines mandate comparing new vaccines to the current standard of care when withholding protection would be unethical. Special cases like animal models or controlled human infection models are used when traditional trials are not feasible. Humphries's claim to the contrary is false and misleading.
Vaccine Safety Monitoring Systems
Claim: Humphries implies throughout the interview that vaccines are inadequately monitored for safety after approval and vaccines are never withdrawn from the market once licensed.
Reality: This claim ignores the existence of robust, multi-layered vaccine safety monitoring systems that operate continuously in the United States and globally.

The U.S. employs several complementary systems that work together to detect even rare adverse events, such as:
1. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS): A passive surveillance system that accepts reports from anyone, serving as an early warning system to detect potential safety signals
2. Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD): An active surveillance system that analyzes healthcare data from over 12 million patients annually to rapidly detect safety signals
3. Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment (CISA): A network of vaccine safety experts that conducts clinical research and evaluates complex safety concerns
4. Biologics Effectiveness and Safety (BEST) Initiative: Uses electronic health records and administrative claims data covering over 100 million people to monitor biologics, including vaccines
These systems have repeatedly demonstrated their effectiveness by identifying extremely rare adverse events that would otherwise be impossible to detect in pre-licensure trials. For example:
The detection of an increased risk of intussusception with the first rotavirus vaccine (RotaShield), which led to its withdrawal (1 excess case per 10,000 vaccinated infants)
The identification of an unusual clotting disorder following adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccines (3.83 cases per million doses of Johnson & Johnson/Janssen COVID-19 vaccine)
The detection of rare cases of myocarditis following COVID-19 mRNA vaccination (varies substantially by age, sex, and vaccine dose, but across the entire population, ~12.6 per million for second doses of mRNA vaccine, less for first and third doses)
When potential safety concerns are identified, they are thoroughly investigated by independent scientific committees. This rigorous post-marketing surveillance provides ongoing reassurance about vaccine safety and enables the medical community to continually refine recommendations based on real-world data (e.g., for COVID-19 vaccination in younger males, observational data suggested a longer interval between first and second doses decreased the risk of myocarditis, so the recommendation was changed to separate the doses to 8 weeks apart), in some cases causing withdrawal of a vaccine as was the case for Rotashield (a fact that Humphries denies has ever occurred in the podcast). In fact, here are more examples of vaccines withdrawn from the market:
We stopped using DTwP once we got acellular pertussis vaccines because of their lower reactogenicity
We replaced a Hib polysaccharide vaccine with a Hib conjugate vaccine because it was much more effective
We no longer routinely vaccinate against smallpox because we eradicated it
We stopped using the oral polio vaccine after we eliminated polio because the risk of VAPP was no longer acceptable (after it had been eliminated)
We removed plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccines because the newer methods to make them were much safer
We removed the killed measles vaccine when it was shown to not work and result in enhanced respiratory disease
We removed a rabies vaccine that was grown in neural tissue with one grown in cell culture because of safety concerns
We removed an adjuvanted live attenuated influenza vaccine from market when it was shown to increase the risk of bell’s palsy
Importantly, even very serious adverse events (e.g., thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome can be fatal in roughly half of cases if not recognized early and promptly treated) need to be weighed against the benefit of the vaccines- which means that even if they are associated with a very serious adverse event, if it is very rare, it may not warrant abandoning the vaccine or withdrawing it. Ideally, you can create a contraindication for a particular portion of the population to receive it if you know they have a disproportionate risk of the adverse event e.g., administration of measles vaccines to severely immunocompromised people can cause measles inclusion body encephalitis, which is fatal in 75% of cases- so severely immunocompromised people cannot receive measles vaccines (and to ensure this, they are screened for immunodeficiency at birth with the heel prick test).
The existence of these systems directly contradicts Humphries's implication that vaccine safety isn't adequately monitored after approval.
🧠 Bottom line: Multiple robust vaccine safety monitoring systems exist, including VAERS, VSD, CISA, and the BEST Initiative, which detect rare adverse events post-vaccination. These systems have identified issues like intussusception with RotaShield and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome with the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, leading to refined recommendations or vaccine withdrawal when necessary. Despite rare serious events, these systems provide ongoing reassurance and contradict claims that vaccine safety isn't adequately monitored after approval.
Vaccine-Associated Kidney Failure and Hypertension (6:40-8:07)
Claim: Vaccines cause kidney failure and hypertension.
Reality: Humphries specifically mentions pandemic influenza vaccine in connection with kidney failure. While isolated case reports exist for some vaccines being given before the development of renal failure, many of these have very obvious alternative explanations. For example, one case involved rhabdomyolysis (i.e., muscle death- which injures kidneys) in a patient who received an influenza vaccine while also on fibrates and cerivastatin - cerivastatin was withdrawn because it frequently causes rhabdomyolysis.
The most that can be said about these isolated reports is that such reactions are exceedingly rare, if not coincidental (and when you do something to hundreds of millions of people, some things will happen in association with one another just by random chance), and no epidemiological evidence supports a link between influenza vaccines and kidney failure.
While Humphries cites a 2025 pharmacovigilance study that detected potential signals for kidney events following COVID-19 vaccination, the study itself acknowledges critical limitations that prevent establishing causality. Most importantly, the research failed to control for prior or concurrent COVID-19 infection, which is independently known to cause significant kidney damage through multiple mechanisms (i.e., acute lung injury, sepsis, hemodynamic alterations, cytotoxic effects, cytokine release syndrome, rhabdomyolysis, coagulopathy, microangiopathy, and collapsing glomerulopathy). The virus can also cause kidney damage through direct infection of kidney podocytes and proximal tubular cells via the angiotensin converting enzyme pathway, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, acute tubular necrosis and protein leakage. Research shows that pathological changes in kidney cells include "degeneration of vacuoles, swelling of cells, accumulation of the SARS-CoV-2 virus inclusion bodies in renal tubular epithelial cells, and delamination of these cells."
The pharmacovigilance study simply analyzed spontaneous reports without comparison to baseline rates or consideration of confounding factors. The authors themselves caution that using their findings to decrease perceived vaccine benefits “could pose a significant risk” and emphasize that the absolute risk remains extremely small– just 6,378 kidney-related reports among more than 13 billion vaccinated individuals worldwide. Proper epidemiological studies with appropriate control groups would be necessary before drawing any causal conclusions and none, to our knowledge, have established a causal relationship between vaccines and kidney failure.
Moreover, vaccination is particularly critical for patients with renal insufficiency because they are immunocompromised to varying degrees. Metabolites from reduced renal function inhibit the generation of B cell responses that produce antibodies. Some patients may also directly lose antibodies in the urine, heightening the risk posed by infectious diseases.
Regarding hypertension, robust evidence for a link is lacking for vaccines being a contributor, though multiple vaccine-preventable diseases have been linked to hypertension. Rare case reports of hypertension within minutes of vaccination fail to support a plausible physiologic explanation (as this is too fast for the vaccine to be the cause- depending on how many minutes, patients wouldn’t even be producing spike antigen at that point, let alone having meaningful systemic inflammation or an antibody or T cell response).
🧠 Bottom line: Claims linking influenza vaccines to kidney failure or hypertension are unsupported by strong evidence. Isolated case reports are rare and lack plausibility in many instances of the vaccine being the driver as alternative explanations, such as the use of other medications, offer more parsimonious explanations. Humphries refers to a 2025 study citing potential kidney disease signals from COVID-19 vaccines, but this lacks proper controls and fails to establish causality, especially when considering COVID-19’s known kidney damage. Vaccination is crucial for those with renal insufficiency, who are more vulnerable to infections. No robust evidence supports a link between vaccines and kidney failure or hypertension.
Medical Education on Vaccines (8:07-9:28)
Claim: "We're not told to take a vaccine history in medical school."
Reality: Humphries lures people in with the fallacy that all medical learning is completed in medical school. This fundamentally misrepresents how medical education works in the United States. While the foundations are laid in medical school, the majority of patient-centered clinical learning occurs during residency and fellowship training.
Vaccination history is a standard part of the medical history every medical student learns in the first year of medical school and is expected to consider performing in every patient encounter for the rest of their careers. Medical school accreditation in the U.S. explicitly requires clinical learning experiences. All accredited U.S. medical schools include structured clinical clerkship experiences, typically after completion of pre-clerkship didactic learning. These clerkships provide students with supervised patient care experience where they learn to take comprehensive medical histories, including immunization histories when clinically relevant.
Vaccine history taking is explicitly taught in several contexts:
During pediatric clerkships, where immunization status is a standard part of well-child visits
In preventive medicine rotations, where vaccine schedules and indications are core content
In family medicine training, where routine health maintenance includes immunization review
During infectious disease rotations, where vaccine-preventable diseases are studied
As with all aspects of the medical history, vaccine history is reviewed with appropriate clinical context: during well visits, when evaluating for vaccine-preventable diseases, before administering vaccines, or when planning immunosuppressive treatments. There is no need to review vaccine history for every single patient encounter (such as acute injury treatment), but it is absolutely part of standard medical training for clinically relevant situations.
🧠 Bottom line: The reality is that vaccine history is standard in the medical school curriculum, and that medical education is a continuum from medical school through residency and beyond, with continuous learning throughout a physician's career as new vaccines and recommendations emerge. Humphries's claim reveals either a profound misunderstanding of medical education or a deliberate attempt to undermine public trust in physicians' training.
Financial Incentives for Vaccination
Claim: While not explicitly stated in this interview, a common anti-vaccine narrative suggests that doctors push vaccines for profit.
Reality: This claim fundamentally misrepresents the economics of vaccine administration. Far from being a profit center, vaccines actually represent the second-highest expense for pediatric practices after staff salaries.
A comprehensive study found that more than half of pediatric practices either break even or lose money on vaccinations. Practices serving higher proportions of Medicaid patients experience particularly significant financial losses due to inadequate reimbursement rates that often fail to cover the total costs of vaccine acquisition, storage, administration, and waste.
The financial challenges are so severe that nearly 10% of pediatricians have seriously considered discontinuing vaccine services altogether. Vaccines require:
Significant upfront capital investment (often tens of thousands of dollars)
Specialized refrigeration equipment with temperature monitoring
Insurance against potential losses from power outages
Dedicated staff time for inventory management and reporting
Secure storage space
Comprehensive documentation systems
Meanwhile, reimbursement is often delayed, inadequate, or complicated by billing challenges. The business model for vaccines is so challenging that many practices describe them as a "loss leader" – a service provided despite minimal profitability because it's an essential component of pediatric care.
This reality directly contradicts the narrative that physician vaccine recommendations are financially motivated. Rather, physicians continue to provide vaccines despite the economic challenges because of their commitment to preventing serious diseases. If profit were the primary motivation, many practices would have already abandoned vaccination services.
We'll publish a more detailed post on this topic in the future, though you can already find some related materials in our existing content.
🧠 Bottom line: If profit were the primary motivation, many practices would have already abandoned vaccination services. The financial incentives argument falls apart under scrutiny of the actual economics of vaccine delivery in medical practice.
Polio History (09:28-17:41)
Claim: Polio never went away; the diagnostic criteria were changed.
Reality: Humphries claims at various points that what was called polio is actually Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) or transverse myelitis (TM). This is absolutely false.
To begin with, we can recover and culture poliovirus from those that have poliomyelitis (stool is the highest yield source of virus, but it can occasionally be recovered from the cerebrospinal fluid, CSF, of poliomyelitis patients). We can also inoculate susceptible animals with poliovirus and watch them develop poliomyelitis. This is not the case for any other condition.
Polio is a virus that, when causing poliomyelitis, infects and causes death of the cell bodies that (via signals through peripheral axons) cause muscle to contract (these cells are referred to as lower motor neurons). Guillain-Barré Syndrome is an autoimmune condition that - often reversibly - damages the myelin insulating the peripheral axons of lower motor neurons. In other words, polio and GBS are distinct processes, in separate locations, with contrasting treatments and divergent prognoses. They even cluster in different seasons: one of the most common risk factors for GBS is gastroenteritis from the bacteria Campylobacter jejuni, which peaks in the wintertime, whereas polio exploded in the summertime.
While a single publication reported several children with paralytic polio whose initial presentation resembled GBS, they generally appear clinically distinct:
GBS classically presents with symmetric sensory loss and paralysis that appears to the patient as if it is ascending from the feet; paralysis polio is more likely to be asymmetric and affecting the proximal muscles
Paralysis in poliomyelitis progresses much more rapidly - often within hours from first symptoms to complete limb paralysis; GBS typically evolves over days to weeks
Spinal poliomyelitis does not affect sensory neurons - sensation remains intact. Sensory deficits will be detectable in GBS except in rare variants
CSF studies for poliomyelitis show increased leukocytes and mildly elevated protein; GBS classically has markedly elevated protein with minimal or normal leukocyte counts
Electrophysiologic evaluation (often referred to as EMG) of affected limbs in polio and GBS will identify different locations and types of nerve dysfunction
Dysautonomia (autonomic nervous system dysfunction) is common in GBS, but rare in paralytic polio
With regard to TM, though this condition can in some cases be caused by infection with polio, it too is clearly distinct from the condition poliomyelitis:
TM is defined by the fact that it involves an entire transverse segment of the spinal cord. Poliomyelitis is confined to the ventral horn where the motor neurons lie. This difference can be seen on MRI imaging.
TM may begin as flaccid paralysis but often progresses into spastic. Polio causes primarily flaccid paralysis.
TM tends to cause symmetric weakness. Polio is generally asymmetric.
Sensory symptoms are also common with TM, but do not occur with paralytic polio.
Upper motor neuron signs are generally present with TM but unusual for polio (spasticity, clonus, hyperreflexia).
🧠 Bottom line: Trained clinicians do not have difficulty differentiating between poliomyelitis, TM, and GBS- all of them are distinct from one another and cases where presentations overlap are the exception, rather than the rule (and diagnostic testing can differentiate them in such cases). Clinical presentations consistent with GBS are approximately as prevalent now as before the elimination of polio. On the other hand, presentations characteristic of poliomyelitis occur over 99.9% less frequently since vaccine introduction in the 1950s. To conclude that polio vaccination is not responsible for preventing poliomyelitis is either a lie or a mind-boggling logical fallacy.
Claim: DDT was a cause of polio.
Reality: This claim has been thoroughly debunked by epidemiologists and medical historians. There is no correlation between DDT use patterns and polio outbreaks in either timing or geographic distribution. This was at one point based on a misconception that polio was spread by flies, which at times led to massive DDT spraying during polio epidemics to try to mitigate spread. Most significantly, the polio epidemics of the early 20th century began before widespread DDT use, and polio cases declined dramatically following vaccine introduction while DDT use continued in many areas. Correlations between polio epidemics and DDT use are poor- the peak of polio epidemics post-vaccine was in 1952 but DDT use peaked in 1959 and does not correlate with polio incidence:
Humphries also fails to explain why polio affected specific age groups or why it occurred in seasonal patterns typical of enterovirus transmission.
🧠 Bottom line: There is no correlation between DDT patterns and polio incidence in timing or geography. Polio epidemics predated widespread DDT use, and cases declined significantly after the introduction of the polio vaccine. This refutes the possibility that DDT can be a cause of polio.
Claim: 95 to 99% of polio cases are asymptomatic (originally made by Rogan, but affirmed by Humphries).
Reality: This is incorrect. About 70% of polio cases in children are asymptomatic. Approximately 0.5-2% cause paralysis, 2-8% cause aseptic meningitis, and 24% cause a minor, nonspecific flu-like illness.
The risk of symptomatic infection is multifactorial with older ages at infection generally having poor outcomes, and pregnancy also being associated with worse outcomes.
Soundbites like this erase critical context. Though the probability of a bad outcome at the level of individual infections with polio represents a very minor fraction of cases, applied to the scale of the population, you still see devastating epidemics of paralysis.
Claim: Tonsillectomies cause severe polio.
Reality: This is not a baseless claim, but Humphries's categorical phrasing in the podcast paints a misleading picture. In the early and mid-20th century, researchers noted a connection between tissue injury and increased risk of paralysis in the injured area. For example, bulbar poliomyelitis (affecting the brainstem) was frequently seen after tonsillectomy, and paralysis sometimes occurred at injection sites. This "provocation poliomyelitis" phenomenon was later demonstrated to reflect direct viral introduction into peripheral nerve axons, allowing the virus to infect the proximal cell bodies, a nuance completely missing from Humphries's oversimplified narrative.
Claim: "Poliovirus is commensal."
Reality: This claim fundamentally misunderstands basic microbiology. Commensal organisms are elements of the normal microbiota present in healthy individuals, typically because they confer some benefit to the host (in simpler terms, these are "friendly" microorganisms that naturally live in or on our bodies without causing harm, and often providing benefits) and they naturally persist on the body unless disrupted by another force e.g., an antibiotic. Poliovirus is unequivocally a pathogen and is not commensal.
One of the standards for something being a commensal is that the immune system should tolerate its presence (at least within its natural site within the body). While poliovirus shedding in the stool can last weeks, fundamentally, the virus will be cleared by the immune system because it induces a robust immune response that eradicates the infection. Immunocompromised people can shed poliovirus in their stool for decades after oral polio vaccine (OPV) administration, representing a public health risk. There is absolutely no evidence for poliovirus conferring any beneficial function to human hosts.
While many infections can be asymptomatic, this does not make the microbe responsible a commensal. Many dangerous pathogens can cause asymptomatic infections while still being capable of causing severe disease in others or in different circumstances. The absence of symptoms does not define a commensal relationship.
🧠 Bottom line: Poliovirus is not a commensal organism. Commensals are harmless or beneficial microbes that naturally coexist with the host, while poliovirus is a pathogen that causes disease. Polio fails to meet anything resembling this definition.
Claim: Humphries references a study of the Xavante Indians supposedly conducted by the Indian Health Services to support her claims about polio being a commensal.
Reality: Humphries's account contains multiple factual errors that fundamentally undermine her credibility. The studies she references make no mention of Indian Health Services involvement. She confuses the U.S. Indian Health Services (a division of HHS) with the Brazilian Indian Protection Agency—a basic error that reveals either carelessness or deliberate misrepresentation.
The actual research she references completely fails to support her claims. For one, the study mainly evaluated antibody responses against a number of infections, including poliovirus. The presence of antibodies does not indicate a current encounter- it reflects a previous encounter, which may have been severe but recoverable. Alternatively, if they had died because poliovirus paralyzed their diaphragm, obviously they would not appear in a serosurvey. The work in no way supports that poliovirus is a commensal- by her reasoning, influenza, smallpox, tuberculosis, and any other pathogen could be described as a commensal. Additionally, other related studies showed a complete absence of antibodies to type 1 poliovirus among various tribes, which means even if her line of reasoning were valid, she’s cherry picking.
Claim: Vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV) or vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP) is the most common cause of polio today.
Reality: While technically accurate, this statement is profoundly misleading without proper context. Vaccine-derived polio cases only exist because the wild poliovirus has been successfully eliminated from most of the world through vaccination campaigns. Wild poliovirus types 2 and 3 have been certified as globally eradicated, with type 1 remaining endemic only in Afghanistan and Pakistan as of 2023.
The incidence of paralysis from oral polio vaccine (OPV) is extremely rare—approximately 1 case per 2.7 million doses—and dramatically lower than the rate of paralysis from wild poliovirus infection (1 in 200, but as high as 2% in epidemics). Importantly, there is no risk of vaccine-derived poliovirus with the inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) used in most developed countries.
In the United States, OPV use was discontinued only after wild poliovirus had been eliminated from the Americas, at which point the risk of VAPP outweighed the benefits of OPV use with IPV available. This represents responsible public health decision-making based on risk assessment, not evidence of vaccine failure as Humphries implies.
When Humphries conflates today's rare vaccine-derived cases with the devastating epidemics of the pre-vaccine era, she creates a false equivalence that ignores the tremendous success of the global polio eradication initiative, which has reduced polio cases worldwide by more than 99.9% since 1988.
🧠 Bottom line: Vaccine-derived polio cases are extremely rare and only occur because wild poliovirus has been nearly eradicated through vaccination. The risk of paralysis from oral polio vaccine (OPV) is minimal compared to wild poliovirus infection, and there is no risk with inactivated polio vaccine (IPV). The U.S. switched from OPV to IPV after wild poliovirus was eliminated, reflecting responsible public health decision-making. Humphries falsely equates rare vaccine-derived cases with the devastating pre-vaccine epidemics, overlooking the success of the global polio eradication initiative.
Microbial Evolution (17:41-19:42)
Claim: Microbes in nature naturally lose their virulence.
Reality: Though it has become something like popular lore, this statement fundamentally misrepresents evolutionary biology and infectious disease dynamics. While the "avirulence hypothesis" (that pathogens steadily evolve toward less virulence over time to maximize host resources that they can parasitize) was once widely accepted, this is no longer the case, with modern research demonstrating that microbial evolution is far more complex. The avirulence hypothesis has largely been abandoned, but the virulence trade-off hypothesis still persists, which argues that pathogens evolve to an optimal level of virulence to maximize their transmission. Nonetheless, even the trade-off hypothesis has mixed evidence.
Viruses frequently evolve to become more virulent in nature. For example:
The Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 evolved to become more deadly than the ancestral strain, with approximately 133% higher risk of hospitalization and death. In fact, the best evidence we have suggests that SARS-CoV-2 has not ever decreased in virulence from the ancestral variant, because even Omicron has comparable disease severity to it (the difference is the presence of immunity attenuates Omicron’s virulence). Anyone in the population who has no immunity to Omicron faces danger comparable to what they would have against the ancestral variant.
Rabbit hemorrhagic viral disease became progressively MORE lethal, probably because the virus is spread by blowflies feeding on rabbit carcasses, and quicker death accelerated its spread. Rabbits also began to evolve enhanced resistance to the virus.
Any time a virus jumps across species and causes disease in the new host, it is a direct instance of evolving enhanced virulence (it goes from being unable to cause disease to being able to cause disease). And this happens all the time, and we are seeing it play out in real time with H5N1 avian flu.
Microbes do not evolve toward reduced virulence unless that reduction confers enhanced transmissibility. In principle, selection for this would be greatest for microbes that kill their hosts so rapidly that they don’t get an opportunity to transmit to the next one, but this does not apply to the vast majority of infectious diseases. Many infectious diseases in fact spread most before the host has symptoms. In some cases, heightened virulence can be coupled to enhanced reputation; for example, the Delta variant had a mutation in its nucleocapsid protein that drastically increased the amount of virus produced, which enhances its spread between hosts and also between cells (letting it penetrate more deeply into the lung). When high virulence aids transmission or doesn't significantly impair it, pathogens can maintain or increase their virulence indefinitely.
🧠 Bottom line: The idea that pathogens always evolve to become less virulent is outdated. The more current "virulence trade-off hypothesis," which suggests pathogens evolve to an optimal level of virulence for transmission, is still debated. In fact, many viruses, like the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 and rabbit hemorrhagic disease, have evolved to become more virulent than their predecessors. Viruses can also evolve enhanced virulence when they jump species, as seen with H5N1 avian flu. Pathogens may maintain or even increase their virulence if it aids transmission, especially when it doesn’t significantly impair host survival.
Claims About Vaccine-Associated Disease Risk (17:41-19:42)
Claim: Vaccines make you more susceptible to the disease.
Reality: This is not the case for any licensed vaccine, full stop. Historically, there were two cases where this happened:
Formalin-inactivated RSV vaccines were shown to cause enhanced disease, but clinical trials were stopped as soon as this was made apparent, and there was a chilling effect on RSV vaccine development for decades despite the public health importance of the disease.
Killed measles vaccine was shown to cause atypical measles (a more severe form of measles) upon infection and was subsequently withdrawn from licensure.
The example of Dengvaxia has done this in some vaccinees who have not previously had dengue, but this is based much more on the unique biology of dengue infection than the vaccine itself (namely, that dengue is much more severe when infected by a strain different from the first one encountered because of antibody-dependent enhancement). The manufacturer (Sanofi Pasteur) and WHO warned to check for dengue antibodies in vaccinees before giving the vaccine once this risk became apparent, and to only offer it to those who had antibodies so that they could avoid the effect of antibody-dependent enhancement. Unfortunately, this guidance followed well after the vaccine had been approved in some cases, and the pre-licensure trials did not separately consider outcomes for vaccinees with antibodies against dengue and those without them, resulting in some tragic incidents. This vaccine has since been taken off the market due to low demand, and a new Dengue vaccine showing high effectiveness without observed antibody-dependent enhancement across multiple strains has since been discovered.
Some people also like to reference the very rare reports of negative vaccine efficacy for COVID-19 vaccine, particularly those that came when the Omicron variant emerged. This is the result of multiple epidemiological fallacies including a failure to adjust for confounders, and a very short-duration follow-up, which, upon longer observation, no longer demonstrated negative efficacy (though it was low for 2 doses).
No currently licensed vaccine in regular use makes recipients more susceptible to the disease it's designed to prevent and any that have are either withdrawn immediately upon uncovering that to be the case or restricted in their use to those individuals in which this would not occur.
🧠 Bottom line: No currently licensed vaccine causes enhanced disease in regular use. While historical examples like the formalin-inactivated RSV vaccine and killed measles vaccine showed adverse effects, these vaccines were immediately withdrawn upon discovery. The issues with Dengvaxia were linked to the unique biology of dengue and not the vaccine itself, with guidance later issued to prevent harm. Claims of negative vaccine efficacy for COVID-19, especially with Omicron, were based on flawed data and short follow-up but were not sustained over time.
Tonsillectomies and Immune Function (19:42-23:39)
Claim: Humphries promotes vitamin C as an alternative to tonsillectomy and for treating tonsillitis.
Reality: While vitamin C is indeed used to treat scurvy (a direct consequence of deficiency) and in some dermatologic conditions with topical application, there is absolutely no scientific evidence that it can treat tonsillitis. Humphries's claim that gargling with vitamin C solution will reduce tonsil size and eliminate the need for tonsillectomy has no supporting evidence in medical literature.
Furthermore, Humphries neglects to mention the potential harms of excessive vitamin C consumption, which include diarrhea, destruction of red blood cells (fatal in at least one case), and kidney stones (specifically in men). In addition to this, vitamin C can give false negative results on stool guaiac testing (which looks for blood in the stool), can interfere with multiple lab tests used to make health assessments, and can cause fatal arrhythmias in patients with iron overload. Other than the prevention of scurvy and its use dermatologically, the clinical benefits of vitamin C are not apparent.
This pattern of promoting unproven "natural" treatments while exaggerating vaccine risks represents a dangerous double standard that could lead patients to reject appropriate medical care.
Claim: Humphries suggests tonsillectomies severely compromise immune function and increase disease susceptibility.
Reality: Tonsillectomies do not cause poliomyelitis as Humphries implies, but there is a relationship between the two. Polio virus has an affinity for injured tissues, and tonsillectomies could make polio more likely to reach the tonsils and use them as a route to access the CNS via the cranial nerves, potentially causing bulbar paralysis. However, this is fundamentally different from claiming tonsillectomies themselves cause disease.
Humphries neglects to mention multiple scientific studies on this topic. Research shows tonsillectomy does not affect serum antibody levels, and individuals who have undergone the procedure have similar responses to live attenuated influenza vaccine as those with intact tonsils. A systematic review and a meta-analysis found no meaningful negative consequences of tonsillectomy on immune function.
While a large Danish study did find an increased risk of respiratory, allergic, and infectious diseases post-tonsillectomy, the challenge with such research is determining causality—whether the conditions observed were caused by or coincidental to tonsillectomy. Tonsillectomy is most commonly performed for recurrent infections of the tonsils or obstructive sleep apnea, meaning patients may already have underlying health issues. In fairness, the study considered this and did attempt to control for this confounding in its design, but residual confounding is always possible.
Additionally, some people's tonsils can regrow after removal, which theoretically should mitigate harmful consequences of their removal.
As with all medical procedures, tonsillectomy should be performed only when benefits outweigh risks—a nuanced approach absent from Humphries's one-sided portrayal.
🧠 Bottom line: Humphries makes two unsubstantiated claims about tonsillectomies: that vitamin C can replace this procedure without evidence, and that tonsillectomies severely compromise immune function. Multiple scientific studies contradict her claims, showing no significant impact on immune function or antibody levels after tonsillectomy. While she correctly notes that injured tissues can make viral entry more likely, she misleadingly suggests the procedure itself causes disease. This represents another case of selectively presenting information while ignoring contradictory evidence, creating a misleading portrayal of a common medical procedure.
Aluminum Adjuvants and Food Allergy (23:39-25:33)
Claim: Humphries states, "It's very well known that the vaccines that have aluminum in them skew the immune system" and claims this causes food allergies when children consume certain foods around vaccination time.
Reality: This claim fundamentally misrepresents basic immunology. For allergic reactions to occur, IgE antibodies must be cross-linked on mast cell surfaces by the allergen. Because aluminum adjuvants induce high levels of IgG against the antigen, these antibodies compete with IgE, actually preventing binding with the antigen. This is precisely why aluminum salts are frequently used in allergen immunotherapy to treat allergies.
The rise in food allergies is multifactorial, likely related in part to early guidelines that advised abstaining from allergenic foods in early life—recommendations that were intended to prevent sensitization but actually increased risk. Whether (and the extent to which) the apparent increase represents better recognition or a true rise remains debated. Current research suggests sensitization rates (the rates at which people develop allergic antibodies to food) haven't substantially changed over time.
While a preliminary CDC study suggested a possible link between exposure to aluminum-adjuvanted vaccines and asthma, these results could not be replicated in Denmark, which has large linked databases that enable more detailed examination medical records. Moreover, the exposure to aluminum from vaccines is minimal compared to ubiquitous environmental exposures, or use of certain antacids, raising serious questions about the biological plausibility of such claims.
Humphries also seems to have basic knowledge gaps about the toxicology of aluminum, claiming it is eliminated in sweat. Aluminum is overwhelmingly renally excreted.
By presenting this mechanism as established fact rather than a fringe theory contradicted by immunological and epidemiological evidence, Humphries misleads listeners about the relationship between vaccination and allergies, potentially discouraging life-saving immunizations based on unfounded fears.
🧠 Bottom line: Humphries uses inflammatory, fear-mongering language about "horrid things" in vaccines without specifying what substances she means. This vague scaremongering is designed to generate fear rather than promote informed decision-making. Aluminum adjuvants have been used safely for nearly a century, and other adjuvants were developed not because of safety concerns but because scientists were seeking to enhance vaccine effectiveness.
Breastfeeding and Immunity (25:33-29:40)
Claim: Humphries states that breast milk contains HAMLET proteins that are "made lethal to tumors" and claims it fights off pertussis and other bacteria. She claims "stem cells are coming through that mother's milk" and that breast milk transfers cellular immunity.
Reality: While breast milk is indeed beneficial for infant health, Humphries significantly exaggerates and misrepresents the scientific understanding of its properties. HAMLET (Human Alpha-lactalbumin Made LEthal to Tumor cells) is a complex of alpha-lactalbumin and oleic acid that has shown promising anti-cancer properties in laboratory settings, but clinical applications remain experimental and limited. The claim that it's "being used by the oncology industry" is misleading as it's still primarily in research phases.
Regarding immune transfer, while breast milk does contain antibodies (primarily secretory IgA) and various immune factors that help protect infants, the mechanism is much different than described by Humphries. Breast milk contains some immune cells, but the significance of their presence as far as infant outcomes is unclear- most of the reported clinical effects from breastmilk seem to be explainable by the presence of secretory IgA, both as direct protection but also through its modulation of microbiome composition. The concept of "dialyzable leukocyte extract" (DLE), aka transfer factor, has very limited supportive data (mainly a single study of leukemic children with varicella), and efforts to research it are tainted by a history of fraud. It is not impossible that transfer factor could have true clinical effects, but it remains poorly characterized and the evidence base is simply far too limited to make strong conclusions about its therapeutic potential.
The PROBIT study, a large randomized trial that approximates a randomized trial of breastfeeding (ethical constraints prevent directly studying breastfeeding in a randomized manner), found moderate benefits for reducing gastrointestinal infections and eczema but did not demonstrate the dramatic immune-boosting effects Humphries describes, and did not show a benefit for respiratory infections (which is the exact result that first principles of immunology would predict). We could find no evidence for the claim that breastfeeding changes the immune response to vaccines from being Th2-predominant to Th1-predominant, and this lacks plausibility because Th1 responses in infants are repressed via multiple mechanisms and do not reach adult-like responses even after 2 years, and Th2 responses are extremely difficult to repress in infants.
🧠 Bottom line: While breast milk offers health benefits, claims about its cancer-fighting properties and immune boosting effects go beyond the data. HAMLET is still experimental, and the concept of "dialyzable leukocyte extract" lacks sufficient evidence. The PROBIT study found moderate benefits of breastfeeding for gastrointestinal infections and eczema, but the effect sizes were not huge. Humphries’s claims about breastfeeding altering immune responses in infants are not supported by current scientific understanding.
Smallpox Vaccine Misinformation: From "Pure Lymph" to Denial of Eradication (29:57-42:21)
Claim: Humphries makes multiple outrageous claims about smallpox vaccines, including that the smallpox vaccine didn't eradicate smallpox and that cows used for smallpox vaccine production were handled by butchers who developed pemphigus as a result. She describes historic vaccines as "Pure Lymph, which was pus that came out of the horse's foot or a donkey's pus skin or a cadaver of a human or a cow's ulcerating udders... scraped into glycerin" and calls smallpox eradication "a fairy tale" and "a joke."
Reality: These claims represent dangerous historical revisionism and profound scientific ignorance. Firstly, the pemphigus claim is scientifically incoherent. Pemphigus is an autoimmune disease—it has no established connection to handling vaccinated animals, and it is not a transmissible disease of cows. There is a form of pemphigus known as “endemic pemphigus foliaceus,” but it is still an autoimmune disease- it is not transmissible; it is known as endemic because it occurs more frequently in certain parts of the world and is associated with insects that feed on blood and has genetic risk factors and has not been associated with transmission through blood products. This statement demonstrates Humphries's fundamental misunderstanding of both immunology and medical history.
The part about ulcers scraped into glycerin is an allusion to animal vaccines. Before animal vaccines and vaccine farms, smallpox vaccination was carried out on an arm-to-arm basis i.e., you would use the lesions formed in a vaccinated person and transfer them to an unvaccinated person. Using animal-derived vaccines had several advantages over arm-to-arm vaccination: it wouldn't transmit syphilis or other human diseases, ensured constant vaccine supply even without spontaneous cowpox cases, and allowed large-scale vaccine production. Nevertheless, smallpox vaccines largely preceded the era of pharmaceutical regulation for most of their history, so there is validity to the claim that they could be adulterated with all sorts of things. In 1901 in particular, there was an incident in which smallpox vaccines were contaminated with tetanus bacteria, which resulted in the deaths of 9 children. That led to the Biologics Control Act of 1902, which eventually resulted in the creation of the FDA.
Humphries's claim that "every Dryvax specimen on the planet" was ordered destroyed to “hide the evidence” that it was a horsepox vaccine represents conspiracy thinking. Firstly, Dryvax was not a horsepox vaccine- the vaccinia viruses contained within it had genetic similarities to horsepox. Saying Dryvax was a horsepox vaccine is like saying that humans are macaques. Dryvax was replaced with ACAM2000 primarily for safety advantages, as Dryvax contained a swarm of vaccinia strains that varied in virulence and was still produced by the animal vaccine method.
Humphries also at one point claims we have no idea what the smallpox vaccine contains because it became its own quasi-species. The smallpox vaccines contain vaccinia virus (VACV), whose genetic ancestry is complex, with some research suggesting possible horsepox origins. The reality is that even in Jenner’s era, horsepox viruses were used to carry out vaccination as well, and there were smallpox vaccines using horsepox. Importantly, orthopoxviruses induce cross-protective immunity against one another, making the specific orthopoxvirus and strain less important for protection than the vaccine’s safety and efficacy.
While the smallpox vaccine can be transmitted from person to person, this typically requires direct contact with the vaccination site or contaminated items (fomites). Applying povidone iodine on day 7 post-vaccination reduces virus shedding without harming the immune response, and contagion ends when the scab falls off. No general follow-up is required after smallpox vaccination unless there is a specific medical reason for doing so (e.g., severe reactogenicity or an adverse event).
Her claim that smallpox was only fatal because of poor living conditions is contradicted by historical evidence. Even in eras with improved living conditions, the overall case fatality ratio for smallpox was 30% (looking at variola minor, variola major, hemorrhagic smallpox, and malignant smallpox), with significant variation based on the form of smallpox. Unlike measles, where vitamin A deficiency clearly profoundly affects outcomes, no such micronutrient relationship has been identified for smallpox. It’s also worth noting that smallpox (were it still occurring today) is not easy to treat and has never been easy to treat. Even today, treatment options for smallpox and other orthopoxviruses are limited, mostly involving supportive care and measures to limit transmission. There are a few antivirals but they tend to have significant toxicity risks. TPOXX (tecovirimat) has been used for mpox and is shown to be effective in culture, but has not demonstrated an improvement in clinical outcomes in trials. Immunoglobulin therapy can be helpful, but since the disease has been eradicated for decades, finding immunoglobulin pools with high levels of anti-smallpox antibodies is not trivial.
Dismissing the eradication of smallpox—a devastating disease that killed hundreds of millions throughout history and was eliminated through a coordinated global vaccination campaign—as a "joke" and "fairy tale" reflects either profound ignorance or a deliberate rejection of one of humanity's greatest medical achievements. This dangerous historical revisionism could undermine public trust in vaccination generally if believed.
🧠 Bottom line: Humphries's claims about pemphigus, smallpox vaccination, and its history are scientifically and historically inaccurate. Pemphigus is an autoimmune disease with no link to vaccinated animals. Smallpox vaccination evolved to improve safety and vaccine supply, and Dryvax was replaced by ACAM2000 because of the latter’s superior safety profile, not destroyed as part of some conspiracy. Smallpox's high fatality rate was not solely due to poor living conditions, and despite advances, it remained a deadly disease, and even today has limited treatment options. Dismissing the global success of smallpox eradication is a level of denialism that verges on delusion.














